ex2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
char* c_pointer = "hello";
char c_array[10] = "hello";
printf("%s\n", c_pointer);
printf("%s\n", c_array);
c_array[0] = 'w';
c_array[1] = 'o';
c_array[2] = 'r';
c_array[3] = 'l';
c_array[4] = 'd';
printf("%s\n", c_array);
c_pointer = (char*) malloc(sizeof(char) * 10);
strcpy(c_pointer, "hello");
printf("%s\n", c_pointer);
return 0;
}
Memory allocation
Code

Static data
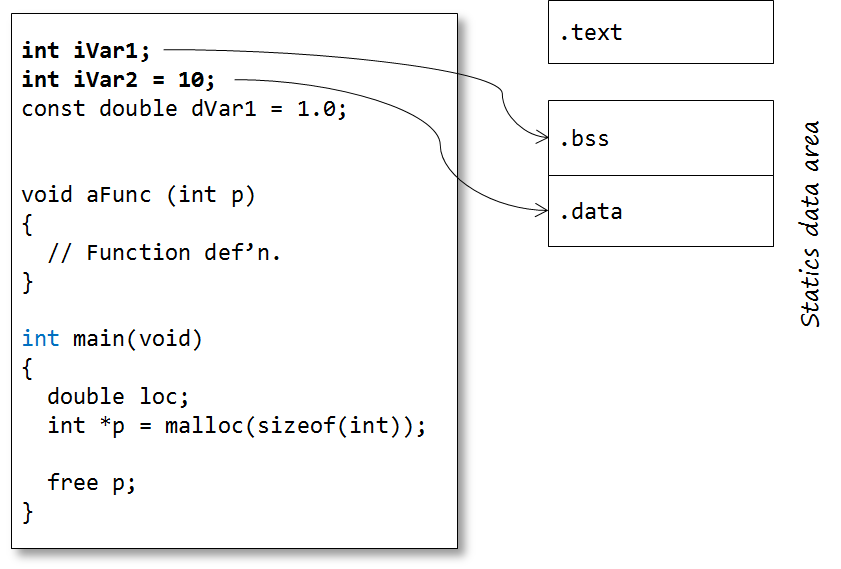
Constants
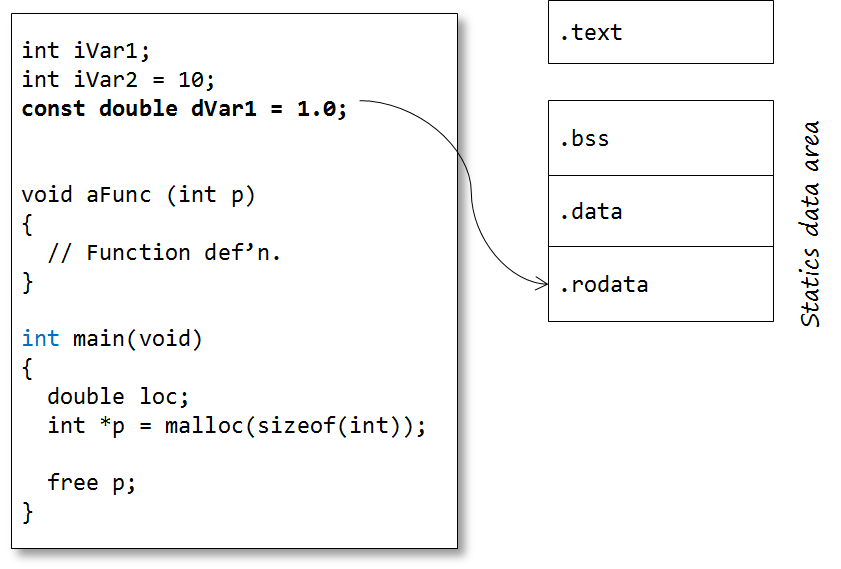
Automatic variables 所謂的stack
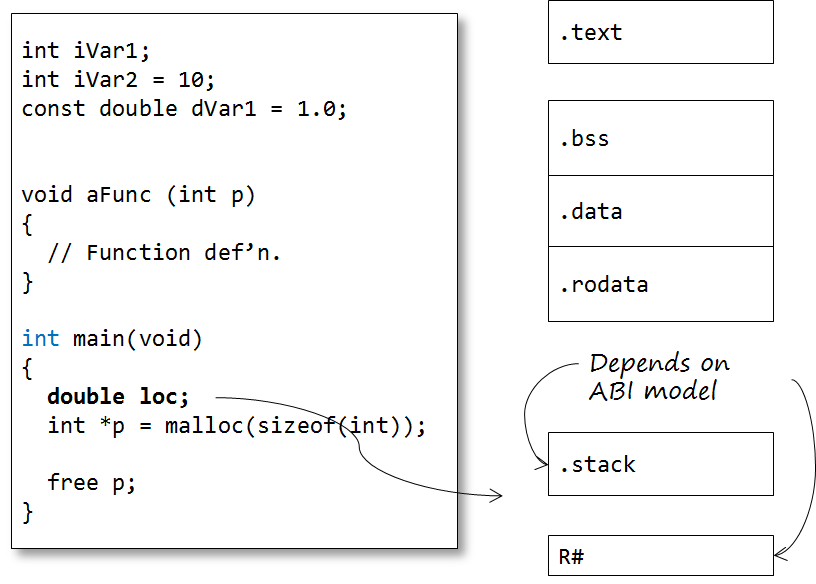
Dynamic data 所謂的heap 由 c 語言malloc or c++ new 動態配置出來的記憶體

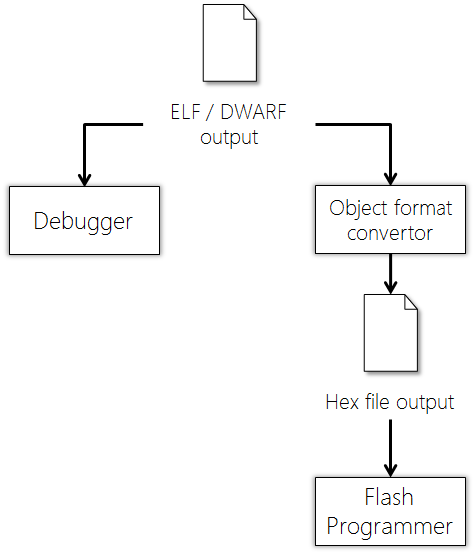
Linker control
- 會把很多object file 裡面 data bss text stack heap rodata 分類集中到ELF(linux 執行檔格式)中對應的 data bss text stack heap rodata區塊
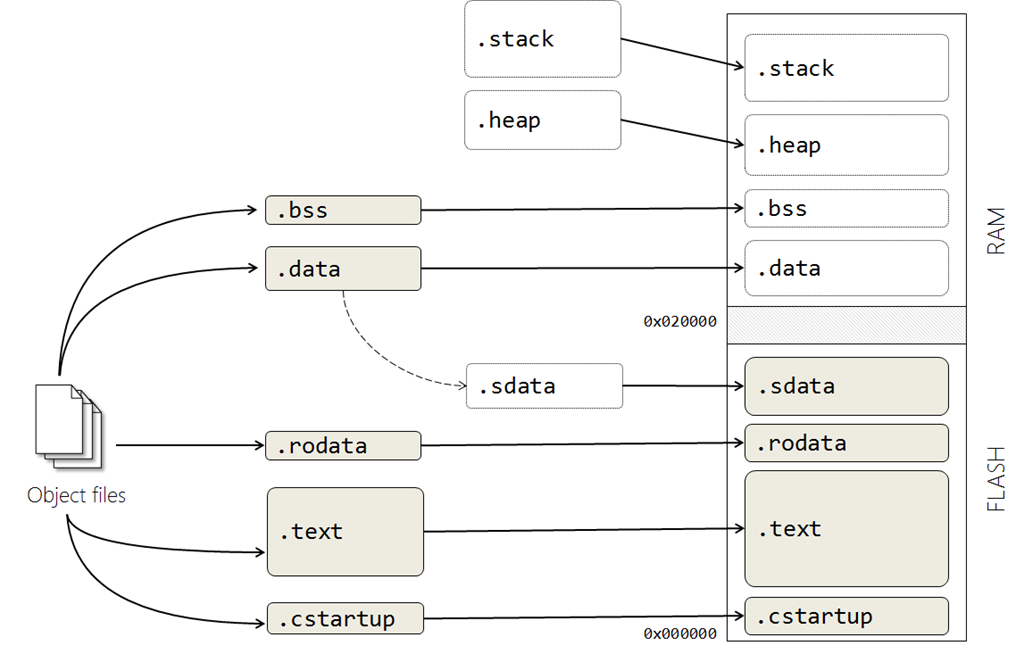
Loading
Reference
https://blog.feabhas.com/2012/06/the-c-build-process/






